Throughout the year, the RBI has effectively managed inflation and sustained strong economic growth. Unlike 2022’s trend of rate hikes, 2023 has seen a notably steady interest rate environment. With the Federal Reserve signaling potential rate cuts in 2024, the RBI may follow suit, adopting a more dovish approach. How will this shift affect investors? This report, backed by historical data, provides insights.
Market Reaction and Trends in Response to Rate Cuts
The market reaction to potential interest rate cuts by central banks has been fervent as investors recalibrate their strategies. The prospect of lower interest rates has underpinned market optimism, with a noticeable impact on various segments of the equity market. Large-cap stocks, traditionally considered more stable and less susceptible to interest rate fluctuations, have illustrated resilience and moderate gains. At the same time, mid-cap and small-cap stocks, often more sensitive to interest rate shifts, have experienced pronounced upwards momentum, reflecting investor confidence in the potential for increased returns in a lower interest rate environment.
Moreover, historical trends and data analysis have shown that in the aftermath of interest rate cuts, the market often witnesses increased activity and substantial price appreciation. This paradigm shift in interest rate dynamics carries significant implications for investors seeking to optimize their portfolios for heightened market returns. Understanding the nuanced impact of rate cuts on different market segments can empower investors to make informed decisions and capitalize on emerging opportunities.
Delving into Sectoral Implications and Investment Opportunities
An imperative aspect of assessing the impact of interest rate cuts on market returns lies in analyzing how various sectors respond to this fundamental shift. Historically, sectors such as real estate, consumer durables, and automobile industries have exhibited heightened performance subsequent to interest rate reductions. This dynamic can be attributed to increased consumer spending, improved borrowing conditions, and enhanced investment sentiment.
Conversely, sectors reliant on fixed-income instruments, such as banking and financial services, may experience a marginally adverse impact due to compressed interest rate differentials. Understanding these sectoral implications can provide valuable insights into identifying potential investment opportunities aligned with the prevailing interest rate environment.
The potential for interest rate cuts holds significant implications for market dynamics and investment strategies. By evaluating historical trends, analyzing market reactions, and discerning sectoral implications, investors can navigate the evolving landscape with confidence and position themselves to capitalize on emerging opportunities.
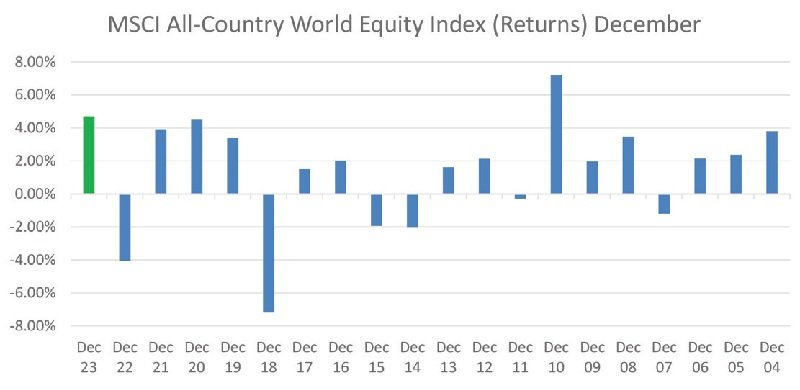
The Potential Impact of RBI’s Interest Rate Cuts on Market Returns
In the latter part of 2023, the global equity market experienced a bullish surge, with a notable uptick in the MSCI All-Country World Equity Index. The primary driver behind this massive upswing is the significant shift in interest rate expectations, influenced by recent data indicating a rapid decline in inflation across Western economies. This consensus on a substantial decrease in borrowing costs for the upcoming year has sparked a bond market rally, luring investors towards equities in pursuit of amplified returns.
The prevailing sentiment in the market now points to six anticipated rate reductions by both the Federal Reserve and the European Central Bank by the end of 2024, representing a remarkable departure from previous concerns about enduring high rates. Moreover, the Indian equity market has exhibited exceptional performance, reflected in the 15.07% gain of the Nifty 500, which includes Large-Cap, Mid-Cap, and Small-Cap stocks, in the final two months of 2023.
The U.S. 10-year Treasury yield, a crucial barometer inversely correlated with bond prices, has declined significantly from over 5% in October to 3.87% due to the sustained dwindling of inflation. This, in turn, strengthens the attraction of equities for investors seeking better returns.
The confluence of factors, including the U.S. Federal Reserve’s actions and India’s domestic triggers such as robust GDP growth numbers and favorable state elections, has led to the outperformance of the Indian equity market compared to many others.
The potential aftermath associated with the impending rate cuts by RBI demands careful consideration, especially with regards to various interest rate cut trends. Investors and market participants must gauge the reactivity of different segments of the market, including Large-Cap, Mid-Cap, and Small-Cap stocks, to these changes. The response of each segment to the interest rate cuts and its resultant effect on overall market returns must be closely monitored and analyzed.
It is imperative for investors to remain vigilant and adaptable as the market dynamics evolve in response to the anticipated rate cuts. Understanding historical trends and reacting judiciously to the potential impacts of these rate reductions on market returns will be instrumental in navigating the forthcoming market environment.
The market’s positive upheaval due to shifting interest rate expectations underscores the need for a comprehensive understanding of the potential implications on market returns, particularly for various segments such as Large-Cap, Mid-Cap, and Small-Cap stocks. It is essential for investors to remain astute and well-informed amidst this evolving landscape.

Market Returns and Interest Rate Cut Trends
The impact of interest rate cuts on market returns can vary based on a multitude of factors. While conventional wisdom often suggests that lower interest rates lead to a bullish stock market, historical data reveals a more complex relationship. It is essential to analyze the historical market reactions to interest rate cuts and understand the subsequent performance of different sectors to identify potential investment opportunities in the current scenario.
Historical Analysis: A Look at Sensex Movement and Policy Rate Cuts
A historical analysis of the Sensex movement in relation to key policy rate cuts since 2000 provides valuable insights into the market’s response to interest rate fluctuations. By examining how the stock market has reacted to previous rate cuts, investors can gain a better understanding of potential market behavior in the wake of upcoming rate adjustments.

Differential Impact on Market Segments
The impact of interest rate cuts on various market segments, including large-cap, mid-cap, and small-cap stocks, warrants careful consideration. While lower interest rates generally stimulate economic activity, the effects on different market segments can vary. Large-cap stocks, known for stability and established market presence, might respond differently to interest rate changes compared to mid-cap and small-cap stocks, which are often more sensitive to market fluctuations.
Optimizing Returns in Varying Market Conditions
Understanding the potential impact of interest rate cuts on large-cap, mid-cap, and small-cap stocks is crucial for investors seeking to optimize returns in diverse market conditions. An analysis of historical trends and sector-specific performance can provide valuable insights into the anticipated behavior of different market segments in response to changing interest rates.
RBI’s Role and Market Expectations
With expectations of potential rate cuts by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI), the market sentiment is keenly attuned to the central bank’s policy decisions. As the domestic economy navigates the current rate cycle, the RBI’s actions and communications play a pivotal role in shaping market expectations and investor sentiment.
Balancing Economic Objectives: Stability and Growth
Balancing the objectives of economic stability and growth, the RBI’s approach to interest rate adjustments holds significance for market participants. Anticipating the central bank’s response to prevailing economic conditions and global interest rate trends can provide valuable insights for investors positioning their portfolios to capitalize on potential market movements.
The interplay between interest rate cuts, market reactions, and the performance of different equity market segments presents a nuanced landscape for investors to navigate. Analyzing historical trends, evaluating sector-specific responses, and monitoring central bank policies are integral to making informed investment decisions in an evolving market environment.
Market Reaction to Interest Rate Cuts
The impact of interest rate cuts on the stock market is a subject of great interest and speculation among analysts and investors alike. Historically, it has been observed that rate cuts by central banks, such as the Federal Reserve or the Reserve Bank of India (RBI), tend to have a positive effect on market returns. Lower interest rates can incentivize investors to move away from traditional fixed-income securities towards equities, as the potential returns on stocks become comparatively more attractive. This shift in investor sentiment often leads to increased demand for stocks, thus contributing to upward momentum in equity markets.
Given the Reserve Bank of India’s pivotal role in determining interest rate policies, the market closely monitors its decisions and communications for indications of potential rate cuts. The RBI’s actions and statements not only affect domestic market sentiment but can also have broader implications for global investors. As such, understanding the RBI’s stance on interest rates and its potential impact on market dynamics is crucial for investors positioning themselves effectively in the Indian equity market.
Understanding the differential impact of interest rate cuts on various categories of stocks is crucial for investors seeking to optimize their portfolios. Large-cap stocks, typically representing well-established companies with stable earnings, may experience increased investor interest due to their comparatively lower risk profile in a declining interest rate environment. On the other hand, mid-cap and small-cap stocks, which often exhibit higher growth potential but also higher volatility, can attract substantial attention as investors seek higher returns in a low-interest-rate scenario.
Impact of RBI’s Interest Rate Cuts: A Market Analysis
In the financial landscape, the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) wields a potent tool in shaping economic dynamics: the interest rate. By manipulating the cost of borrowing, the RBI endeavors to stimulate investment, spending, and borrowing, fostering the conducive conditions for robust economic growth.
Market Turbulence and Reaction
In times of financial turbulence, the stock market often bears the brunt of the storm. A case in point is the recent crisis, where the market witnessed significant double-digit declines, rippling across diverse sectors. A dive into the data reveals a sobering reality: the performance of various sectoral indices exhibited a marked downturn in the lead-up to the interest rate cut, signaling widespread market distress.
Post-Rate Cut Resurgence
However, the script took a turn post the interest rate cut in 2020. In the six months following this pivotal event, the indices not only clawed back from their previous losses but also charted impressive gains. Of particular note were the staggering 56% surge in the BSE Information Technology index and the 55% upswing in the BSE Auto index during this period.
Robust Momentum and Exceptional Returns
Zooming out to the one-year mark post rate cut, a pattern of staggering momentum and exceptional returns emerged. Major sectoral indices sparked into life, igniting a blaze of returns for discerning investors. The BSE Information Technology index stole the show with an astounding surge of over 100%, while the BSE Auto index and BSE Realty index raced ahead with gains of 96% and 84% respectively.
Looking Ahead: Forecast and Opportunities
As we delve deeper into each period, a compelling picture begins to crystallize, shedding light on the equity market’s potential returns. The landscape post interest rate cuts appears promising, opening avenues for proactive investors seeking handsome returns.
In the next segment, we will explore the factors underpinning this market resurgence and unearth the underlying trends, equipping you with insightful forecasts and actionable intelligence.
This in-depth market analysis reveals the transformative impact of RBI’s interest rate cuts and the ensuing market dynamics. With captivating returns beckoning, the financial horizon brims with opportunities for those primed to harness this shifting economic tide.
Initial Rate Reduction and Preceding Quarter Performance
In examining the impact of the RBI’s first rate cuts on the stock market, a historical review of rate adjustments and stock market movements was undertaken, focusing on their diverse components. Notably, throughout the last seven instances of initial policy rate decreases commencing from the year 2000, the majority of these first cuts were foreshadowed by downturns in the S&P BSE 500 index, with declines ranging from 18.74 percent to 29.4 percent. This pattern was particularly pronounced during events such as the technology bubble in the early 2000s, the global financial crisis in 2008, and more recently, the upheaval caused by the coronavirus pandemic. Among the seven interest rate cuts under scrutiny, the S&P BSE 500 index exhibited an average decline of 12.5 percent in the period between the first rate cut and three months prior to it.
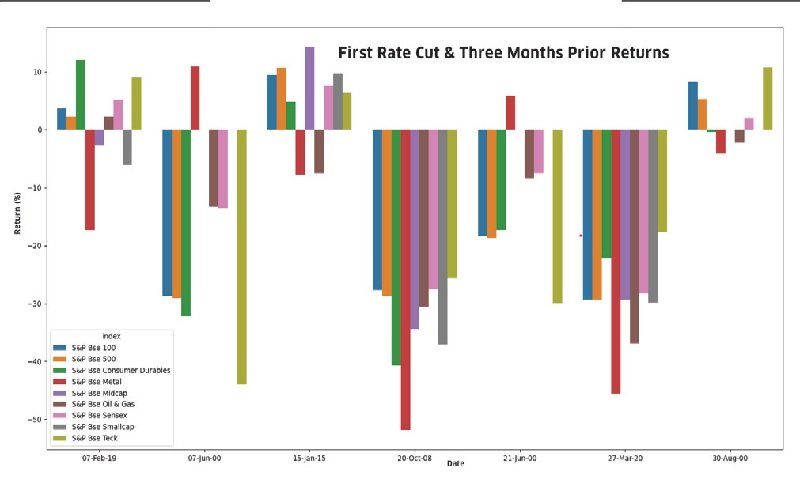
In a typical economic landscape devoid of major disruptions, diverse indices have historically demonstrated positive performances, particularly in the wake of rate cuts initiated by the RBI. For instance, prior to the initial rate reduction in January 2015, indices exhibited an average gain of 5.23 per cent over the preceding three months. Similarly, leading up to the rate cut in February 2019, the average gain across various indices stood at 2.3 per cent, indicating favorable market sentiments. Notably, despite these overall positive trends, the metal index emerged as a consistent underperformer during these periods.
Rate Cut and Six Months after Returns
The aftermath of the RBI’s rate adjustments witnessed a myriad of outcomes across equity indices in the subsequent six months. There was no discernible uniformity in the returns, with indices such as the S&P BSE 100, 500, small-cap, and mid-cap intermittently displaying negative returns. Notably, in specific instances, these indices showcased pockets of positive movements, notably observed following the pandemic-induced turmoil. Conversely, the S&P BSE Oil and Gas index exhibited more consistent positive performance, with a majority of movements reflecting positive trends.
Furthermore, the S&P BSE Sensex and Teck indices demonstrated varying trajectories, albeit primarily tending toward negative returns in the aftermath of rate cuts. On the other hand, the S&P BSE metal and consumer durables indices portrayed mixed performances, featuring both positive and negative returns. Despite this diverse array of outcomes, the average returns across all indices exhibited a marginal positive bias, indicating an overall favorable market response to the rate adjustment.
This data underscores the nuanced and intricate reactions exhibited by distinct equity segments following monetary policy modifications, thus highlighting the profound impact of market volatility and sector-specific dynamics on the overall market landscape. The varying responses elucidate the multifaceted interplay between interest rate alterations, market behaviors, and the idiosyncratic characteristics of different industry sectors.

Impact of Rate Cuts on Market Returns after One Year
Following the initial RBI rate hike, the subsequent year saw positive performance across diverse equity indices. Notably, the S&P BSE 100 and 500 initially experienced significant declines in value but demonstrated a notable recovery, yielding substantial positive returns. A standout example is the remarkable growth witnessed in indices like S&P BSE metal and small-cap during years such as 2008 and 2020, far exceeding their initial negative performances.
While some sectors such as oil and gas and consumer durables displayed more modest recoveries, the overall average returns across all indices suggest an upward trajectory, signaling a predominantly positive trend. With average returns ranging from 6.93% to 51.44% across various indices, there is clear evidence of a significant rebound from the initial losses. This underscores the resiliency of the market post rate hikes, indicating its capacity to not only recover but also thrive over a one-year period, despite the initial market turbulence.

Impact of Rate Cuts on Different Key Sectors
Banking, Financial Services and Insurance (BFSI) Sector
The impact of rate cuts on the BFSI sector is multi-faceted. While a decline in lending rates may exert pressure on banks’ profit margins, it can also stimulate borrowing and increase demand for loans, providing support to the financial sector. However, lower interest rates may impact investment returns for insurance companies, posing challenges to their profitability. Additionally, individuals reliant on interest income from savings accounts or fixed-income investments may experience diminished returns due to the decline in interest rates.
Consumer Spending and Retail Sector
Lower interest rates act as a catalyst for increased consumer spending by reducing the cost of borrowing. This can lead to reduced interest burden, potentially freeing up more disposable income for consumers and boosting retail sales. The positive impact extends to various retail sectors including clothing, electronics, home goods, and automotive industries. Lower rates can also enhance the affordability of fast-moving consumer goods (FMCG), sustaining or increasing sales of essential products like food, beverages, and personal care items.
The unique interplay of rate cuts with distinct sectors underscores the intricacies of market dynamics, prompting a nuanced understanding of the broader economic landscape. As interest rate adjustments continue to reverberate across varied industries, investors and market participants must closely monitor these developments to navigate the evolving financial terrain effectively.
Real Estate and Construction Sector
Reduced interest rates have a notable impact on the real estate and construction sector. The lowered interest rates serve as a catalyst for increasing housing demand by making mortgages more affordable, which in turn can lead to heightened property sales and potentially elevated property prices. The commercial real estate sector also experiences positive effects as businesses seeking to expand or invest in properties benefit from lower borrowing costs. Real Estate Investment Trusts (REITs) with substantial debt are poised to gain from reduced interest rates as it decreases their borrowing costs. However, a prolonged period of low-interest rates may raise concerns of an overheated real estate market, potentially leading to speculative behavior and inflated property prices.
Information Technology Sector
The recent stance of the Federal Reserve to maintain interest rates while hinting at potential rate reductions in 2024 has resulted in a robust rally for domestic IT majors. This optimism has bolstered the sector as the majority of revenue for these companies is derived from the U.S. markets. Reduced interest rates typically lower the cost of capital for IT companies, enhancing their capacity to invest in research and development, adopt new technologies, and undertake expansion projects. Low-interest-rate environments often stimulate mergers and acquisitions within the IT sector, fostering industry consolidation and heightened competitiveness. Furthermore, a depreciating domestic currency due to lower interest rates can improve the global competitiveness of IT exporters, potentially boosting international demand for IT services and products.
Reduced interest rates have significant implications for the real estate, construction, and information technology sectors. While the real estate sector benefits from increased housing demand and lowered borrowing costs, caution is warranted to prevent speculative behavior and inflated property prices. Conversely, the IT sector experiences enhanced capabilities for investment, industry consolidation, and improved global competitiveness, all contributing to potential growth and expansion.
Each sector responds uniquely to changes in interest rates, presenting both opportunities and challenges. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for investors and stakeholders navigating the evolving financial landscape.
Impact of Rate Cuts on Different Capitalisation Tiers
Large-Cap Stocks
Large-cap stocks are often perceived as bastions of stability and are less susceptible to interest rate fluctuations compared to their smaller counterparts. When interest rates are low, large-cap stocks stand to benefit from reduced borrowing costs, enabling companies to access cheaper capital for expansion and investments. This advantage makes large-cap stocks an attractive option for investors who prioritize stability and consistent dividends in a low-interest-rate environment.
Mid-Cap Stocks
In contrast to large-cap stocks, mid-cap stocks typically exhibit a more pronounced response to economic conditions and interest rate shifts. A decrease in interest rates can have a positive impact on mid-cap stocks, potentially stimulating economic growth due to their heightened sensitivity to consumer and business spending fluctuations. However, if rate cuts are interpreted as a response to economic challenges, mid-cap stocks may face increased volatility, reflecting the market’s uncertainty.
Small-Cap Stocks
Small-cap stocks, known for their heightened sensitivity to interest rate fluctuations and economic conditions, stand to benefit from reduced borrowing costs in a low-interest-rate environment. This can fuel increased capital spending and business growth. However, during times of economic uncertainty, small-cap stocks face heightened vulnerability to market downturns, potentially making them more susceptible to broader economic concerns, wherein rate cuts may not suffice to counter market apprehensions.
These distinct reactions across different capitalization tiers underscore the nuanced impact of rate cuts on various segments of the stock market. While large-cap stocks may experience stability and enhanced access to capital, mid-cap and small-cap stocks navigate a landscape of heightened volatility and differing responses to economic stimuli. Investors must carefully consider these dynamics when formulating their investment strategies in response to interest rate movements.
Market Reaction and Investor Sentiment
The announcement of a potential rate cut by the RBI has stirred a mix of reactions within the financial markets. While some investors are cautiously optimistic about the potential for reduced borrowing costs, others are adopting a wait-and-see approach, anticipating further clarity on the central bank’s decision-making process. The market’s response to the prospect of a rate cut is indicative of the nuanced interplay between monetary policy and investor sentiment.
Sectoral Implications and Economic Dynamics
In examining the potential impact of a rate cut on different sectors, it becomes evident that varying dynamics are at play. Industries reliant on credit facilities, such as real estate and infrastructure, are likely to benefit from reduced borrowing expenses, potentially catalyzing investment and expansion initiatives. Conversely, sectors sensitive to interest rate fluctuations, such as banking and financial services, might experience short-term volatility as market participants recalibrate their valuation models in response to shifting monetary conditions.
Macro-Level Considerations and Policy Ramifications
From a macroeconomic perspective, a rate cut by the RBI carries implications beyond the immediate realm of equity markets. It has the potential to influence consumer spending patterns, business confidence, and overall economic momentum. Furthermore, the central bank’s decision will undoubtedly reflect its assessment of inflationary pressures, exchange rate dynamics, and global economic trends, thereby shaping its policy stance in the pursuit of price stability and sustainable growth.
Navigating Uncertainty and Risk Management
Amidst the prospect of a rate cut, prudent risk management strategies become paramount for investors and businesses alike. As the interconnectivity of global financial markets continues to underscore the need for adaptability and foresight, stakeholders must assess their exposure to interest rate-sensitive instruments and devise contingency plans to navigate potential market volatility. Proactive engagement with financial advisors and consultants can offer valuable insights into mitigating risk and optimizing portfolio performance in a dynamic interest rate landscape.
Long-Term Investment Outlook and Strategic Positioning
While near-term market movements in response to a potential rate cut are subject to volatility and uncertainty, astute investors maintain a long-term perspective, underpinned by strategic positioning and diversification. By incorporating a holistic investment approach that considers fundamental analysis, sectoral dynamics, and geopolitical factors, investors can align their portfolios with enduring themes and capitalize on opportunities arising from evolving monetary policies.
In conclusion, the anticipation of a rate cut by the RBI has set the stage for a nuanced interplay of market dynamics, investor sentiment, and economic implications. As stakeholders navigate this landscape of shifting monetary conditions, informed decision-making and strategic foresight will be essential in maximizing opportunities and managing risk in a dynamic financial environment.









